The Role of Exchange Rates in the Economy and Financial Markets
Exchange rates can be seen as a kind of bridge connecting domestic economies with foreign and global economies. The exchange rate determines the price at which each country’s goods and services are traded in global markets. A strong currency makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive. Conversely, a weak currency increases export competitiveness and makes imports more costly.
Key factors fundamentally affected by exchange rates include:
Inflation
The exchange rate has a direct impact on the price level and domestic inflation. When the value of the national currency decreases, the prices of imported goods and services rise because imports require more foreign currency.
This increase in import costs gradually spreads throughout the entire economy and causes a rise in the general price level. Thus, a decline in the national currency’s value can be an inflationary trigger, especially in countries that import a large portion of their goods and raw materials. Conversely, a strong currency can make imports cheaper and help control inflation.
Foreign Investment
An unstable and volatile exchange rate can act as one of the most important risk factors for foreign investors. Investors who invest in a country's market, in addition to economic and political risks, must also consider exchange rate fluctuations, because a decline in the value of that country's currency can reduce their investment returns.
Therefore, exchange rate stability and its predictability play a very important role in attracting foreign direct investment and long term investors, and help the economic growth of countries.
Stock Market
Exchange rate fluctuations directly affect the performance of companies and consequently the price of their stocks. Companies that derive a large portion of their revenue from exports will experience higher profitability when the national currency depreciates because their products become cheaper and more competitive in foreign markets.
This usually leads to an increase in the stock prices of these companies. Conversely, companies dependent on imported raw materials or equipment face higher costs and reduced profitability, which can result in a decline in their stock prices. Therefore, exchange rate fluctuations are one of the key risk and opportunity factors in the stock market.
Bond Market
Exchange rate changes can affect interest rates and bond yields, especially for debt securities issued in foreign currencies.
When the national currency depreciates, the cost of repaying these bonds for governments or companies increases, leading to higher interest rates and reduced attractiveness of investing in bonds.Also, changes in the exchange rate can affect foreign investors’ real returns and intensify volatility in the bond market. For this reason, the exchange rate is considered one of the important factors in risk management strategies in the bond market.Forex Market
The forex market is exactly where exchange rates are determined and traded, so the exchange rate plays a central and direct role in this market. Exchange rate fluctuations create many profit opportunities for traders but also carry significant risk. Various factors such as monetary policies, economic data, political events, and changes in global financial markets cause exchange rate movements. Forex traders monitor these changes through fundamental and technical analysis to make accurate predictions about rate movements.
Exchange Rate in the Forex Market and How It Is Determined in Global Financial Markets
The exchange rate, or the conversion price of one currency to another, is one of the fundamental concepts in global financial markets and especially in the Forex market. This rate is usually influenced by various economic factors such as interest rates,Gross Domestic Product (GDP), unemployment rate, and the level of economic activity in each country. In fact, changes in any of these indicators can directly cause fluctuations in the exchange rate.
Currency prices are often determined in a market without a physical location called the Forex or FX market. This market is a global network of banks, financial institutions, investment funds, and retail traders who buy and sell currencies 24 hours a day, throughout the week. For this reason, exchange rates can experience small changes or even large jumps at any hour of the day.
How Is the Exchange Rate Determined in the Forex Market?
The price of each currency in Forex, like in any other free market, is determined based on the principle of supply and demand. If the demand to buy a currency (for example, the euro) increases while supply remains constant or decreases, the price of that currency rises. Conversely, if demand decreases or supply increases, the price falls. This simple yet powerful interaction between buyers and sellers around the world causes constant fluctuations in exchange rates.
Exchange rates are usually displayed using international abbreviations. For example, USD is the symbol for the US dollar, and EUR is the symbol for the euro. When referring to the exchange rate between the euro and the dollar, the currency pair symbol EUR/USD is used. These symbols are employed to accurately represent the exchange rate between two currencies in the global market.
In the Forex market, currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY. This means you simultaneously buy one currency and sell another. For example, if you buy EUR/USD, you are buying euros and selling dollars. The rate of this currency pair indicates how many dollars are needed to buy one euro. If the Eurozone economy is strong or the US dollar weakens, this ratio changes and the price rises.
Who Are the Players in the Forex Market?
It is generally assumed that the Forex market is solely a place for conducting transactions, but it should be noted that the main players in the Forex market are central banks, large financial institutions, hedge funds, multinational corporations, and others. The decisions and behaviors of each of these groups can significantly change supply and demand, causing fluctuations in exchange rates.
Exchange Rate Emerges from the Market
Ultimately, the currency price in the Forex market is the result of a complex and instantaneous interaction among thousands of global players who make decisions influenced by economic, political, and psychological conditions. This characteristic makes the Forex market a dynamic and constantly changing environment that requires precise analysis, financial knowledge, and a correct understanding of market drivers.
Exchange Rate and Influential Factors in Global Financial Markets and Forex
Exchange rate fluctuations reflect numerous factors occurring in the world economy. The exchange rate is a relative indicator expressed as a comparison between the currencies of two countries. Some of the most important determinants of the exchange rate, each with its own significance, include:
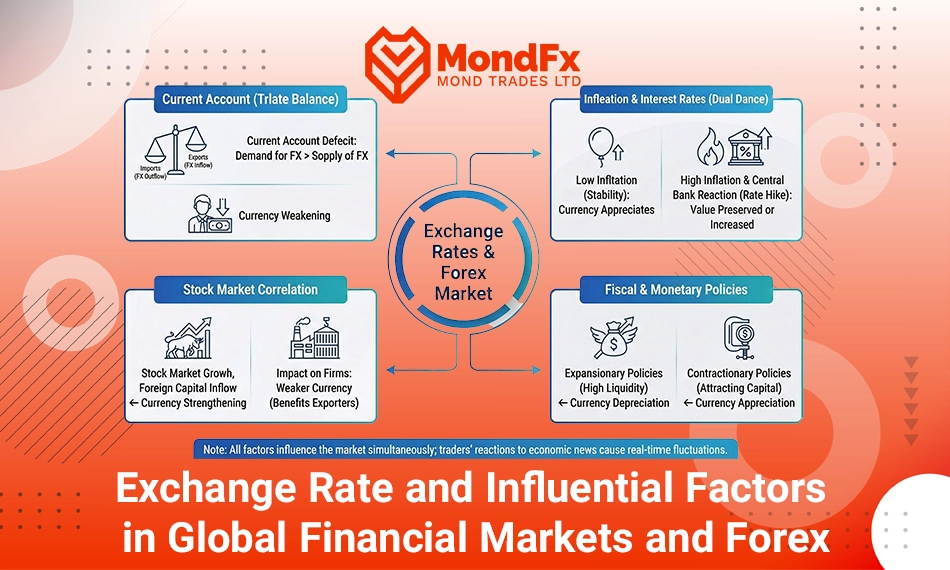
Inflation and Interest Rates in the Forex Market
When a country’s inflation is low, the value of its currency usually increases. This causes the currency of that country to be in higher demand in the Forex market because investors prefer to place their money in a country where the currency is more stable or appreciating. For example, if inflation in Japan is lower than in the United States, Forex traders may prefer the Japanese yen over the US dollar.
On the other hand, high inflation in a country usually leads to a depreciation of its currency against other currencies. However, to combat inflation, the central bank may raise interest rates. An increase in interest rates can be attractive to investors because they earn higher returns from deposits or securities. As a result, even under high inflation conditions, if interest rates rise sufficiently, demand for that currency may still persist.
Therefore, Forex traders simultaneously consider both inflation and interest rates and decide which currency to buy or sell based on the combination of these two factors. This is why economic reports related to inflation, interest rates, and central banks’ monetary policies have a direct and immediate impact on currency price movements in the Forex market.
Current Account
The current account of a country is an indicator of its balance of payments. This indicator shows the flow of money in and out through the export and import of goods and services, the payment or receipt of interest and investment income, and international financial transfers.
Therefore, the current account is defined as an account that determines whether a country is earning income or spending more in its economic and external interactions.
When a country runs a current account deficit, it consumes more foreign currency than it earns. To meet this need, the demand for foreign currencies (such as the dollar, euro, or pound) increases. On the other hand, since exports decrease, the supply of foreign currency declines. This imbalance between the supply and demand for foreign currency causes the price of foreign currency to rise and the value of the domestic currency to fall. In simple terms, the national currency weakens.
In the Forex market, which is a place for buying and selling currencies, traders closely monitor the current account status of countries. If the data show that a country has a large current account deficit, many traders predict that the value of that country’s currency will decline. Therefore, they sell that currency and buy another currency that is expected to strengthen. This behavior of traders itself causes increased volatility in exchange rates.
For example, if the monthly report shows that the UK’s current account deficit has increased, Forex traders may sell the pound and buy the dollar or euro because they expect the pound to depreciate. This market behavior causes the GBP/USD rate to decline.
As a result, the current account deficit not only weakens the national currency but also directly triggers reactions in the Forex market and determines the direction of many traders’ transactions.
Fiscal and Monetary Policies
Fiscal and monetary policies affect the exchange rate in various ways. Expansionary fiscal policies, such as increasing government spending or reducing taxes, usually lead to increased liquidity and inflation. Higher inflation means a decrease in the value of the national currency because its purchasing power declines. Similarly, expansionary monetary policies, such as lowering interest rates or increasing the money supply in the market, also lead to increased liquidity and a decrease in the currency’s value.
On the other hand, contractionary monetary policies, such as raising interest rates, attract foreign investors because they seek higher returns. This increases demand for the national currency and strengthens the exchange rate.
In the Forex market, traders closely react to news and changes related to countries’ fiscal and monetary policies. When the central bank raises interest rates or the government adopts cautious fiscal policies, the value of that country’s currency usually rises, and traders buy that currency.
The Relationship Between Exchange Rates and Stock Prices in Forex
When a country’s stock market grows and performs positively, it indicates a strong and stable economy. Under these conditions, foreign investors tend to invest in that country’s stocks, which means increased demand for that country’s national currency. For example, growth in the US stock market leads investors to buy dollars to purchase stocks, which strengthens the dollar exchange rate in the Forex market.
On the other hand, exchange rate fluctuations directly affect company profitability, and these changes are reflected in stock prices. A depreciation of the national currency usually benefits exporting companies because it increases the competitiveness of their products in the global market, and their stock prices may rise. However, severe exchange rate fluctuations that lead to higher costs of importing raw materials can reduce the profits of importing companies and cause their stock prices to decline.
Forex market traders continuously monitor the stock market because sudden changes in the stock market cause rapid shifts in currency trading. These changes usually result from variations in investors’ risk tolerance and capital flows.
Overall, the relationship between exchange rates and stock prices in the Forex market is reciprocal and complex; stock market growth leads to increased demand for the national currency and its strengthening, while exchange rate fluctuations affect companies’ profitability and stock prices.Summary
Overall, the exchange rate is not merely a number on Forex market charts; rather, it is a direct reflection of economic conditions, fiscal and monetary policies, inflation, the current account balance, and investor behavior on a global scale. Changes in the value of a national currency can affect inflation, the cost of imports and exports, corporate profitability, and even foreign investment flows.
The Forex market, as the intersection point of these factors, is a dynamic and sensitive arena in which exchange rate fluctuations create significant opportunities and risks. On the other hand, the two-way relationship between exchange rates and other financial markets such as equities and bonds shows that precise analysis and a deep understanding of the influencing factors are essential conditions for smart decision making in this market. Ultimately, success in Forex depends on a trader’s ability to monitor economic, political, and psychological factors simultaneously and to anticipate market behavior in response to exchange rate changes.
If you are looking to start a reliable path in the world of trading and financial markets, collaborating with the MondFx team can be a good starting point for building your personal strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is an exchange rate, and why is it important in Forex?
An exchange rate is the price of converting one currency into another, and in the Forex market it is traded as a currency pair. This rate plays a central role because its movements determine investment opportunities and risks and directly reflect economic conditions and fiscal policies of countries.
2) What factors cause exchange rate fluctuations?
Inflation, interest rates, gross domestic product (GDP), current account deficits or surpluses, monetary and fiscal policies, political events, and the performance of equity and bond markets all affect exchange rate movements.
3) How does the exchange rate affect foreign investment?
Exchange rate fluctuations can decrease or increase the returns on foreign investment. Exchange-rate stability and predictability are important factors in attracting long term investors.
4) What is the relationship between exchange rates and the stock market?
Exchange rate fluctuations can affect companies’ profitability and stock prices. A weaker currency usually benefits exporters and harms importing companies, while a stronger currency works in the opposite direction.
5) How is the exchange rate determined in the Forex market?
In the Forex market, exchange rates are determined based on the principle of supply and demand and the real time interaction of thousands of global participants, including banks, financial institutions, multinational corporations, and retail traders.
6) How can exchange rate fluctuations be forecast?
Forecasting exchange rates requires fundamental analysis (economic indicators and monetary policies) and technical analysis (charts and price trends). Traders try to predict the direction of exchange rate movements by combining these two approaches.
7) Why is the exchange rate important for countries’ economies?
The exchange rate directly affects imports and exports, inflation, corporate competitiveness, and foreign investment flows, and is, in a sense, an indicator of a country’s economic health.

