Drawdown (DD) is one of the most important risk management indicators in Forex trading, representing the amount of decline in an account from its highest balance level to its lowest point within a specific period. Understanding drawdown and how to control it can significantly impact a trader’s long-term survival and success.
In this article, we will explore the concept of drawdown, its types, how to calculate it, and strategies to reduce capital decline in Forex trading.
What is Drawdown (DD)?
To put it simply, drawdown (DD) in Forex refers to the amount of capital reduction from the highest account balance (Peak) to the lowest level (Trough) within a given period. This indicator reflects the percentage decrease in an account due to consecutive losses or a drop in asset value and serves as a key metric in risk management and trading performance analysis.
For example, if your account balance drops from $10,000 to $7,000, your drawdown would be:
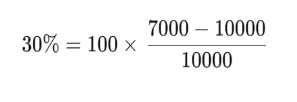
This means a 30% decline in capital relative to the highest recorded balance.
Types of Drawdown in Forex
1. Absolute Drawdown
This metric indicates the capital decline relative to the initial account balance.
Formula:
AbsoluteDrawdown=InitialBalance−LowestBalance
Example:
If your trading account starts with $5,000 and drops to $4,200, the absolute drawdown would be:
5000−4200=800
2. Relative Drawdown
Relative drawdown represents the percentage decline in capital compared to the highest recorded account balance (Peak).
Formula:
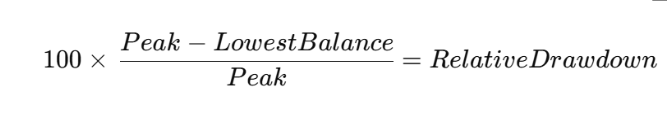
Example:
If your account reaches a peak of $12,000 and then drops to $9,000, the relative drawdown would be:25%
This metric helps traders assess the overall risk level of their trading strategy.
3. Maximum Drawdown (MDD)
Maximum drawdown represents the largest capital decline during a trading period, making it one of the most critical factors for evaluating the performance of a trading strategy.
Formula:
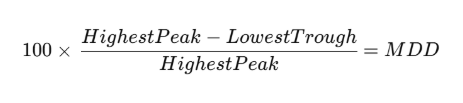
Example:
If your account rises to $15,000 and then declines to $10,000 before recovering, the maximum drawdown (MDD) would be:33.3%
This indicates a 33.3% capital decline from the highest recorded balance.
Why Should We Understand Drawdown?
Understanding drawdown is one of the fundamental principles of risk management in Forex trading, as it can differentiate between a successful trader and a losing one. If drawdown is not controlled, it can lead to the loss of the entire capital and eventual exit from the market.
Reasons Why Understanding Drawdown is Important:
Preserving Capital and Preventing Heavy Losses
Drawdown represents the maximum loss a trader has experienced within a specific period. If the drawdown is too high, the risk of losing the entire capital increases significantly.
Helping to Choose the Right Strategy
Different trading strategies have varying levels of drawdown. Traders aiming to minimize risk and improve trading stability should select strategies with lower drawdown.
Enhancing Emotional Control in Trading
Drawdown can lead to stress, emotional decision-making, and revenge trading. Understanding this concept helps traders manage their trades with a calm and rational mindset.
Better Risk Management and Trade Size Adjustment
By understanding drawdown, traders can adjust their position sizes according to their capital and strategy while avoiding high-risk trades and excessive leverage usage.
Improving Trading Performance and Long-Term Profitability
Minimizing drawdown allows traders to remain profitable in the long run and withstand negative market fluctuations. A strategy with low drawdown is generally more stable and reliable.
Preventing Margin Calls
Excessive drawdown can reduce free margin, ultimately leading to a margin call. Understanding drawdown helps traders avoid overly risky trades that could drain their account.
How to Reduce Drawdown?
1. Setting an Appropriate Stop Loss (Stop Loss Placement)
Using a trailing stop loss to secure profits.
Setting stop loss based on the ATR (Average True Range) indicator.
Avoiding extremely tight stop losses that may trigger premature exits.
2. Implementing Proper Risk Management
Risking no more than 1-2% of total capital per trade.
Diversifying trades to spread risk.
Maintaining a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2 in trades.
3. Reducing Leverage Usage
Using reasonable leverage (maximum 1:10 to 1:20) to avoid large fluctuations.
Monitoring free margin levels to prevent overexposure to large positions.
4. Choosing Low-Risk Trading Strategies
Trading with price action methods and strong technical analysis.
Avoiding revenge trading after losses.
Focusing on trend trading rather than counter-trend trades.
5. Using a Trading Journal and Backtesting
Recording all trades, stop losses, take profits, and risk-to-reward ratios.
Reviewing historical market data to assess the drawdown of a strategy.
Analyzing trading performance to identify and improve weak points.
Drawdown and Professional Capital Management in Forex
Drawdown (DD) is one of the most crucial indicators for measuring risk and capital decline in Forex trading. This concept helps traders control potential losses and extend the lifespan of their trading accounts.
Proper Drawdown Management Includes:
Setting an appropriate stop loss
Applying risk management and using reasonable leverage
Implementing low-risk trading strategies
Keeping detailed trading records and analyzing past trades
What is Relative Drawdown?

Relative Drawdown is one of the key metrics in risk management and evaluating trading strategies in Forex. This indicator represents the maximum percentage of capital decline relative to the highest account balance (Equity Peak) within a specific period.
Unlike Absolute Drawdown, which calculates capital reduction based on the initial account balance, Relative Drawdown expresses the percentage decline compared to the highest recorded balance, making it highly useful for assessing the risk level of a trading system.
How to Calculate Relative Drawdown?
Formula for Relative Drawdown:
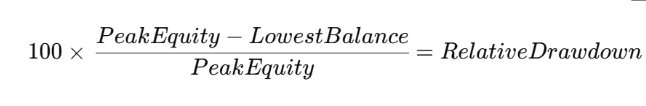
Example:
Suppose your account reaches $12,000 at its peak but then drops to $9,000 after a series of losing trades. The Relative Drawdown would be:25%
This means your account has experienced a 25% decline relative to its highest balance.
Importance of Relative Drawdown in Forex Trading
Evaluating the Risk of a Trading Strategy:
Traders analyzing different strategies should measure their Relative Drawdown. The lower this value, the lower the strategy’s risk.
Controlling Emotions and Managing Capital:
Knowing the maximum relative drawdown helps traders better manage their strategies and avoid emotional decision-making during losses.
Protecting the Trading Account and Extending Capital Longevity:
If Relative Drawdown exceeds 30-40%, the account is at high risk, and the probability of a Margin Call increases significantly.
Enhancing Long-Term Profitability:
Strategies with lower Relative Drawdown are generally more stable and reliable, helping traders achieve sustainable profitability in the long run.
Ways to Reduce Relative Drawdown in Forex Trading
Applying Proper Risk Management:
- Risking a maximum of 1-2% of capital per trade.
- Avoiding excessively high-risk trades.
Setting Stop Loss Based on Technical Analysis:
- Using the ATR (Average True Range) indicator to determine a dynamic stop loss suitable for market volatility.
Reducing High Leverage Usage:
- Using reasonable leverage (below 1:20) to prevent excessive drawdowns.
Diversifying Trades:
- Spreading capital across multiple currency pairs and strategies to reduce the impact of consecutive losses.
Backtesting and Reviewing Trading Strategies:
- Analyzing historical market data to evaluate the Relative Drawdown of a strategy before using it in a live account.
What is Maximal Drawdown (MDD)?
Maximal Drawdown (MDD) is one of the most critical risk management indicators for evaluating trading performance. This metric represents the largest capital decline from the highest account balance (Equity Peak) to the lowest balance (Trough) within a specific period.
To put it simply, Maximal Drawdown reflects the biggest loss a trader has experienced before the account recovered.
How to Calculate Maximal Drawdown (MDD)?
Formula for Maximal Drawdown:
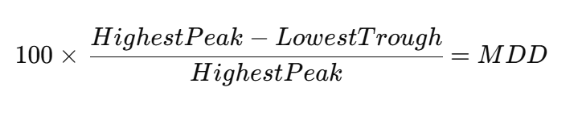
Example:
If your account balance reaches $15,000, but after a series of losses, it drops to $10,000, the Maximal Drawdown would be:33.3%
This indicates that your account has suffered a 33.3% capital decline from its highest recorded balance.
Differences Between Maximal Drawdown and Other Types of Drawdown
Maximal Drawdown (MDD):
- The largest capital decline within a specific period, without considering recovery.
Relative Drawdown:
- The percentage decrease in account balance relative to the highest peak during a period.
Absolute Drawdown:
- The capital decline relative to the initial deposit.
💡 Maximal Drawdown is commonly used as a key metric to assess the risk level of a trading strategy.
Importance of Maximal Drawdown in Forex Trading
Assessing the Risk Level of a Trading Strategy:
Traders who want to evaluate their strategy’s performance must analyze how much their capital has declined at its worst point.
Protecting Capital and Avoiding Margin Calls:
A high MDD means the account is at greater risk and may trigger a margin call.
Determining Trade Sizes (Lot Size):
The lower the MDD, the better the capital management, allowing traders to adjust their trade sizes more effectively.
Measuring Stress Levels in Consecutive Losses:
A high MDD can cause significant psychological stress, leading traders to make emotional trading decisions. Proper risk management techniques are crucial to control this.
How to Reduce Maximal Drawdown?
- Applying Risk Management:
- Avoid risking more than 1-2% of total capital per trade.
- Setting an Appropriate Stop Loss (SL):
- Avoiding stop losses that are too tight or too wide, as they can negatively impact trading performance.
- Using Reasonable Leverage (Leverage Management):
- Instead of using high leverage (1:100 or more), traders should opt for lower leverage (1:20 or below) to minimize excessive drawdowns.
- Implementing Low-Risk Strategies:
- Using long-term trading approaches with controlled risk instead of high-risk, short-term speculative trades.
- Backtesting and Optimizing Trading Strategies:
- Testing strategies on historical data (Backtesting) to analyze the Maximal Drawdown and improve trade settings before applying them in a real account.
What is Absolute Drawdown?
Absolute Drawdown is one of the key risk management indicators in Forex trading, measuring the amount of capital decline relative to the initial account balance. Unlike Relative Drawdown, which is calculated based on the highest balance level during a specific period, Absolute Drawdown only measures the capital reduction from the initial deposit.
How to Calculate Absolute Drawdown?
Formula for Absolute Drawdown:
AbsoluteDrawdown=InitialBalance−LowestBalance
Example:
If a trader starts with a $5,000 account balance and, during a trading period, the capital drops to $4,200, the Absolute Drawdown would be:
5000−4200=800
This means the trader has lost $800 from their initial capital.
Differences Between Absolute Drawdown and Other Types of Drawdown
Absolute Drawdown: Represents the capital decline from the initial account balance. If this value is high, it indicates a high-risk trading approach.
Relative Drawdown: Expresses the percentage decline in capital relative to the highest recorded balance, not the initial deposit.
Maximal Drawdown (MDD): Measures the largest capital decline from the highest peak to the lowest point within a specific period.
Absolute Drawdown is mainly used to analyze early losses in a trading account, whereas Relative and Maximal Drawdown are more relevant for long-term strategy evaluation.
Why is Absolute Drawdown Important in Forex?
Measuring Risk at the Beginning of Trading:
A high Absolute Drawdown indicates poor capital management or the use of high-risk strategies in the early stages.
Assessing the Stability of a Trading Strategy:
Strategies with low Absolute Drawdown tend to be more stable and lower-risk.
Protecting Initial Capital:
Absolute Drawdown helps traders understand how much of their initial investment is at risk and whether adjustments in their trading approach and risk management are necessary.
How to Reduce Absolute Drawdown?
- Apply Proper Risk Management:
- Traders should not risk more than 1-2% of their total capital per trade.
- Set a Logical Stop Loss (SL):
- Adjusting stop loss levels appropriately to prevent excessive capital loss.
- Use Balanced Leverage (Leverage Management):
- Excessive use of leverage (e.g., 1:100 or higher) can increase Absolute Drawdown.
- It is recommended to use leverage lower than 1:20.
- Implement Low-Risk Strategies:
- Choosing trades with a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2.
- Backtest and Optimize Trading Strategies:
- Testing the strategy on historical data (Backtesting) to evaluate Absolute Drawdown before using it in a live account.
Suitable Trading Strategy Based on Drawdown in Financial Markets
Selecting a trading strategy based on drawdown levels is one of the most crucial factors in risk and capital management. Trading strategies with lower drawdown levels tend to be more stable and have a lower likelihood of significant losses. Therefore, to preserve capital and avoid severe account declines, traders should implement methods that keep drawdown at a controlled level.
Characteristics of a Suitable Trading Strategy in Terms of Drawdown
Controlled Drawdown (Less than 20-30%)
- Strategies with over 30% drawdown are considered high-risk and may face difficulties in recovering losses.
Stability in Performance and Reduced Capital Decline
- Strategies that avoid severe drawdowns and have a faster recovery factor are generally more suitable.
Favorable Risk-to-Reward Ratio
- An ideal trading strategy should have a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2 or higher to effectively compensate for potential drawdowns.
Controlled Trade Size and Avoiding High Leverage
- Managing lot size and leverage proportionally to capital helps prevent severe drawdowns.
Backtested on Historical Data
- A strategy must be tested on past market data before applying it in a real account to assess its drawdown levels.
Best Trading Strategies to Reduce Drawdown
1. Trend Following Strategy
Suitable for: Long-term and medium-term traders
Using moving average indicators (MAs) and price action to identify strong trends.
Applying dynamic stop loss based on ATR (Average True Range) to avoid premature exits.
Maintaining a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2 to preserve capital.
2. Breakout Trading Strategy
Suitable for: Swing traders and short-term traders
Entering trades after breaking key support and resistance levels.
Setting stop loss based on previous levels and volume analysis to minimize risk.
Managing positions and partial exits to reduce potential drawdown.
3. Scalping Strategy with Tight Risk Control
Suitable for: Traders with small capital and short-term strategies
Exiting losing trades quickly and closing profitable trades before market reversals.
Using a fixed stop loss of 10-15 pips with a minimum risk-to-reward ratio of 1:1.5.
Avoiding excessive leverage (maximum 1:20) to prevent severe drawdowns.
4. Mean Reversion Strategy
Suitable for: Medium-term traders
Entering trades at overbought and oversold levels with price action confirmation.
Utilizing indicators such as RSI and Bollinger Bands to determine entry points.
Dividing trade size and managing free margin to mitigate capital drawdown risks.
Practical Solutions to Reduce Drawdown in Trading Strategies

- Applying Proper Capital and Risk Management:
- Avoid risking more than 2% of total capital per trade.
- Use logical Stop Loss (SL) and Take Profit (TP) levels based on technical analysis.
- Controlling Emotions and Avoiding Revenge Trading:
- Record all trades in a trading journal to analyze mistakes.
- Focus on trade quality rather than quantity.
- Using Combined Methods to Reduce Risk:
- Integrate price action, technical analysis, and indicators to minimize high-risk trades.
- Divide positions into smaller trades to prevent sudden capital drawdowns.
- Conducting Backtesting and Forward Testing on Trading Strategies:
- Assess the Maximum Drawdown (MDD) and recovery percentage.
- Test the strategy in a demo account before using it in a live trading environment.



