Why Should You Use Fundamental Analysis for Trading?
Fundamental analysis helps you make smarter decisions by deeply understanding the economic and financial factors that impact asset values. Instead of focusing on charts and patterns, this method uncovers the real reasons behind price movements.
By using fundamental analysis, you can estimate the intrinsic value of an asset and identify opportunities where the market price is undervalued or overvalued compared to its actual worth.
In general, if you want a clearer picture of an asset's future and prefer to base your trading decisions on real data, fundamental analysis will be an indispensable tool for you.
Quantitative and Qualitative Aspects of Fundamental Analysis
Quantitative Fundamental Analysis
Quantitative fundamental analysis focuses on measurable, numerical data related to an asset or market. This type of analysis primarily examines tangible financial information, such as a company's financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements) and financial ratios like Price to Earnings (P/E), Earnings Per Share (EPS), and Return on Equity (ROE).
In financial markets such as stocks or forex, quantitative fundamental analysis is commonly used to predict price movements and identify mispriced assets. For instance, in the cryptocurrency market, analysts may use economic indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), interest rates, and inflation to forecast price trends.
Qualitative Fundamental Analysis
In contrast, qualitative fundamental analysis examines non measurable factors that significantly affect asset values. These factors include management quality, brand reputation, market sentiment, and even political or economic conditions. This type of analysis focuses more on social trends and the competitive position of a company or asset.
For example, in the stock market, qualitative analysis may involve evaluating a company's management team, growth strategies, or potential regulatory changes. In forex, qualitative fundamental analysis involves examining changes in central bank monetary policies or the political and economic stability of different countries, which can lead to unexpected currency fluctuations.

The Concept of Financial Statements in Fundamental Analysis
In fundamental analysis, financial statements are one of the primary tools for evaluating the condition of a company or market. These statements provide traders with vital and accurate information that helps them understand the real status of a company and make more informed decisions regarding buying or selling assets.
What Do Financial Statements Contain?
Income Statement
The income statement reflects a company's performance over a specific period. It records revenues and expenses, ultimately revealing how much profit or loss the company has generated during that period. For traders, understanding a company's profitability is crucial. Indicators such as operating profit and net profit provide clear insights into a company's performance and its ability to generate profit.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet shows a company's financial position at a specific point in time. It details the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. For traders, the balance sheet is a tool to assess whether the company has significant debts or if its assets are sufficient to cover liabilities and support future growth. Key financial ratios such as the debt to equity ratio and liquidity ratio are derived from this statement.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement reveals how a company manages its cash. Does it generate cash from operations? Can it pay off debts and invest in its future? This statement is particularly important for assessing a company's liquidity. Even if a company is profitable, poor cash flow management can lead to future difficulties.
The Concept of Financial Ratios in Fundamental Analysis
Financial ratios help traders evaluate a company's financial condition and performance across different metrics. The most important financial ratios include:
Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is one of the most widely used ratios in fundamental analysis, indicating how much investors are paying for each unit of the company's earnings. Simply put, it tells you how much you need to pay for every dollar of the company's profit. A high P/E ratio may suggest that the market has high expectations for the company's growth, but it could also mean the stock is overvalued.
Return on Equity (ROE)
This ratio measures a company's profitability relative to its shareholders' equity. A high ROE indicates that the company efficiently uses its resources to generate profit. For traders, this metric is essential because it shows how well the company is converting its investments into profits.
Debt to Equity Ratio
This ratio compares a company's debt to its shareholders' equity, showing the extent of its reliance on debt financing. A high debt to equity ratio could signal high risk for the company, as a significant portion of its funding comes from debt. While debt can accelerate a company's growth, it may also create significant challenges during economic downturns or financial pressures.
Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Earnings per share is one of the most critical metrics for assessing a company's performance. It shows how much profit the company has earned for each share during a given period. Consistent growth in EPS often indicates a company's financial health and sustainable growth.
Current Ratio
The current ratio measures a company's ability to meet its short term obligations using its current assets. A ratio below 1 suggests that the company may face liquidity issues in the near future.
What is Forex Fundamental Analysis?
Forex fundamental analysis involves examining the economic, political, and social factors of various countries to predict changes in currency exchange rates. This type of analysis is based on economic principles that assess how these factors affect the supply and demand for currencies. Forex fundamental analysts aim to identify strong signals of changes in currency values, which may result from economic events such as interest rates, inflation, or the overall economic conditions of countries.
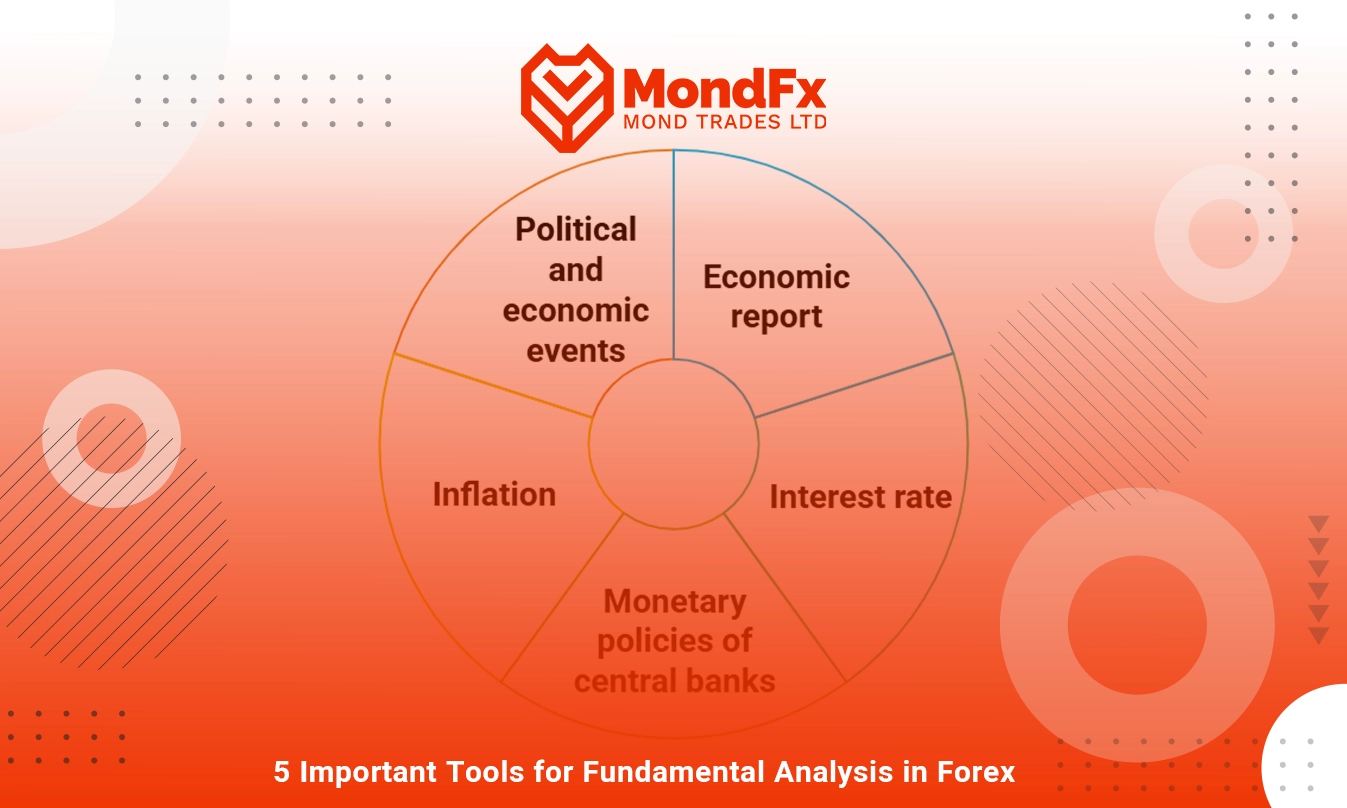
Five Key Tools for Forex Fundamental Analysis
Here are the essential tools for conducting forex fundamental analysis:
Economic Reports
Reports such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), CPI (Consumer Price Index), and NFP (Non Farm Payrolls) are among the most important data points for forex fundamental analysis. These reports reflect the economic status of a country and their impact on the currency market.
Interest Rates
Interest rates are one of the most significant tools used by central banks to control inflation and economic growth. Changes in interest rates can greatly impact currency values, as higher interest rates typically attract foreign investors and strengthen the currency.
Central Bank Monetary Policies
Monetary policies of central banks, such as Quantitative Easing (QE) or tightening policies, can significantly influence currency exchange rates. These policies often result in changes to liquidity, which in turn affects currency prices.
Inflation
Inflation reflects the increase in prices within a country and directly impacts the purchasing power of a currency. Central banks often adjust interest rates to control inflation.
Political and Economic Events
Political events such as elections, crises, or changes in trade policies can significantly impact the forex market. These events often lead to high levels of currency market volatility.
How to Use Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
In forex fundamental analysis, traders use economic and political data to predict changes in the value of one currency relative to another. For example:
Interest Rates: Suppose the U.S. Federal Reserve raises interest rates. This news could strengthen the U.S. dollar because investors seek higher returns from the increased interest rates.
NFP Report: If the U.S. Non Farm Payrolls report shows significant job growth, the U.S. dollar may strengthen as it indicates a healthy economy and increases the likelihood of future interest rate hikes.
Inflation: If a country experiences high inflation, its currency typically weakens. For instance, if inflation in the Eurozone rises, the Euro may depreciate.
By combining these data points, traders can form a comprehensive understanding of market conditions and make informed trading decisions.
Cryptocurrency Fundamental Analysis Training
Cryptocurrency fundamental analysis involves evaluating the value and potential of a cryptocurrency by examining its surrounding economic, technical, and social factors. Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on price data and trading volumes, cryptocurrency fundamental analysis considers factors such as the development team, project technology, market supply and demand, and global economic conditions to determine the intrinsic value and future outlook of the cryptocurrency.
Key Variables for Cryptocurrency Fundamental Analysis
To conduct cryptocurrency fundamental analysis, the following variables are essential:
Development Team and Project
One of the most critical variables in cryptocurrency fundamental analysis is evaluating the development team and programmers behind the project. The team's strength and track record in the blockchain world can significantly influence the project's success.
Technology and Innovation
Cryptocurrencies utilize different technologies. Analyzing technical features and advantages such as scalability, security, and transaction speed are key factors for conducting cryptocurrency fundamental analysis.
Supply and Demand
Like any other asset, supply and demand have a significant impact on cryptocurrency prices. Assessing the total supply and mining rate for each cryptocurrency is crucial to understanding how changes may affect its price.
Market Volatility and Trading Volume
Analyzing market volatility and trading volume can indicate the level of adoption and use of the cryptocurrency in the market.
Resources for Cryptocurrency Fundamental Analysis
Cryptocurrency fundamental analysis requires access to the following resources:
Project Reports
Reviewing official reports and the whitepaper of each project is the first step in fundamental analysis. These documents provide detailed information about the project's goals, strategies, and future plans.
Analytical Platforms
Platforms like CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko are essential sources for precise information about supply, price, and trading volumes of cryptocurrencies.
Media and News
Keeping up with news and developments related to cryptocurrencies from reliable media outlets and social channels can greatly enhance cryptocurrency fundamental analysis.
Steps for Analyzing a Cryptocurrency Fundamentally
Study the White Paper
The first step in cryptocurrency fundamental analysis is studying its whitepaper. This document explains the project's goals, technology, and future prospects.
Analyze the Team and Advisors
Evaluate the development team and project advisors to understand their technical expertise and experience in the blockchain industry.
Examine the Economic Model and Supply
Analyze the cryptocurrency's economic model and the total and circulating supply to understand how it may handle market pressures in the long term.
Assess Community and Public Adoption
Active communities and public acceptance of a cryptocurrency, especially on social media, can help you gauge its popularity among users.
Analyze Competitors and Market Position
Compare the cryptocurrency with similar projects and analyze how it competes in the market. This can provide insights into its potential future position.

