A careful examination of this rate can assist traders and investors in analyzing the overall labor force status and the economic health of a country. Generally, a high employment rate signifies economic prosperity and improved labor market conditions, whereas a decline in this rate could signal economic challenges and rising unemployment within society. Therefore, monitoring changes in the employment rate is crucial for making informed investment decisions and conducting accurate financial market analyses.Why Is the Employment Rate Index an Important Economic Indicator?
The employment rate index is considered a vital economic indicator for several reasons, detailed below:1. Measuring Economic Health
The employment rate represents the percentage of individuals of working age usually between 15 and 65 who are actively employed in the labor market. A high employment rate generally signals economic growth, increased GDP, and an improved standard of living. Conversely, a low employment rate may indicate economic stagnation, reduced production, and a rise in unemployment.2. Impact on Domestic Consumption and Demand
Employed individuals typically have more disposable income, enabling them to purchase more goods and services. This rise in consumption, in turn, boosts domestic demand and contributes to economic growth. Moreover, an increasing employment rate can strengthen the domestic market and enhance overall economic productivity.3. Influence on Economic and Monetary Policies
Governments and central banks adjust their fiscal and monetary policies based on employment rates. For instance, if the employment rate is low, they may lower interest rates or increase government spending to stimulate economic activity. On the other hand, a high employment rate could heighten inflationary pressures, prompting central banks to raise interest rates to keep inflation in check.4. Controlling Inflation and Price Stability
A high employment rate can lead to increased demand for goods and services, potentially driving up prices (inflation). Hence, managing the employment rate through appropriate economic policies can help maintain price stability and prevent excessively high inflation.5. Social Sustainability and Poverty Reduction
A high employment rate significantly contributes to reducing poverty and social inequalities. Individuals actively participating in the labor market can meet their basic needs, leading to greater social stability and diminished interpersonal tensions. Additionally, lower unemployment rates can enhance overall quality of life and boost public satisfaction.6. Attracting Foreign and Domestic Investment
A high employment rate, indicating an active and capable economy, can draw both domestic and foreign investors. Investors typically seek markets with a stable, engaged workforce, which can lead to further economic growth and sustainable development.7. Evaluating Market Performance
As a key labor market indicator, the employment rate helps governments and economic institutions tailor their policies and programs to the market’s actual needs. This index can reveal both the strengths and weaknesses of the labor market, ultimately guiding improvements in employment related policies. Paying attention to these aspects can foster sustainable social and economic development.How to Calculate the Employment Rate
The employment rate is calculated as follows:
Employment Rate = (Number of Employed Individuals / Total Labor Force) × 100 Labor Force:
This term refers to all individuals of working age generally between 15 and 65 who are either actively seeking employment or currently employed in various jobs.Identifying Employed Individuals:
To determine who is employed, consider those who were active in the labor market during a specific time period (usually one month), whether working full time or part time.Types of Employment Rate Indicators
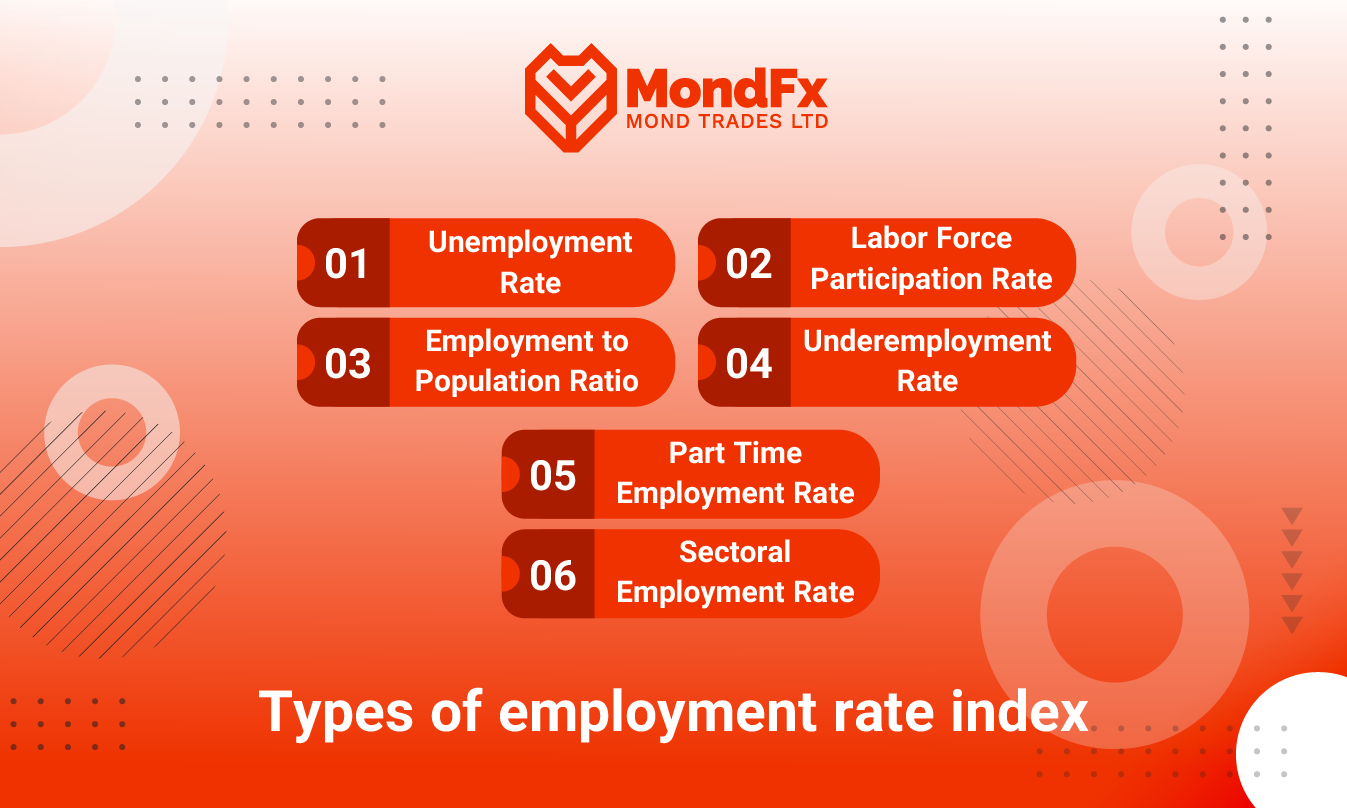
Employment rate indicators help traders and investors make more informed financial and investment decisions by providing a clearer picture of economic conditions. Below are various types of employment rate indicators:1. Unemployment Rate
As one of the key economic indicators, this rate represents the percentage of working age individuals who are actively seeking employment but unable to find suitable jobs. A high unemployment rate generally signals economic challenges, reduced production, and potential social pressures.2. Labor Force Participation Rate
The labor force participation rate refers to the percentage of working-age individuals who are either employed or actively seeking employment. Changes in this indicator can reflect shifts in people’s motivation or ability to enter the job market, helping us understand overall economic dynamics.3. Employment to Population Ratio
This ratio shows the percentage of working-age individuals who are currently employed compared to the total working age population. A high ratio indicates higher employment and economic productivity, whereas a low ratio can warn of economic stagnation and insufficient job opportunities.4. Underemployment Rate
Underemployment rate measures the percentage of individuals who are working in positions that do not fully utilize their skills or those who work more hours than they prefer. This indicator highlights inefficiencies in the labor market and possible structural issues hindering optimal employment.5. Part Time Employment Rate
This rate indicates the percentage of people working part time. While an increase in part-time employment may suggest a flexible labor market, it can also point to a shortage of full time job opportunities.6. Sectoral Employment Rate
This rate illustrates employment across different economic sectors, such as industry, services, and agriculture. analyzing these sector specific rates helps investors and traders identify trends and economic shifts in various industries, enabling better decision making based on sector performance.Factors Affecting the Employment Rate
Several factors can have a significant impact on financial and currency markets:Government Economic and Fiscal Policies
Economic and fiscal policies adopted by governments play a decisive role in creating or reducing employment rates. Measures such as cutting taxes, increasing government investments, and providing financial support to businesses can lead to more job opportunities and higher employment rates. Conversely, strict fiscal policies may reduce investment and increase unemployment.Economic Growth
Sustainable economic growth and higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) are directly linked to increased employment rates. As a country’s economy grows, the demand for labor rises, which in turn boosts employment. Economic growth can result from expanding production in various industries, adopting new technologies, and improving infrastructure.Sanctions and International Restrictions
Economic sanctions can significantly affect employment rates. Limited access to international markets, reduced foreign investment, and decreased exports can lead to higher unemployment and fewer job opportunities. For traders, these conditions may directly impact the value of the national currency and financial markets.Technological Development and Innovation
Technological advancements and industrial innovations can create new job opportunities while rendering some existing positions obsolete. These changes can have a dual effect on employment rates: on one hand, they create jobs in emerging fields, and on the other, they reduce positions in older industries.Education and Workforce Skills
The level of education and skill sets within the workforce are crucial factors influencing employment rates. A skilled and specialized workforce can attract new investments and create higher value added jobs. Conversely, a lack of necessary skills can hinder people’s employment prospects and drive up unemployment rates.Political and Social Stability
A country’s political and social stability can directly affect investment inflows and create a conducive environment for businesses. Political unrest, corruption, or lack of trust in the government may hinder economic growth and job creation. For traders, these issues can signal potential volatility in financial and currency markets.Labor Market Policies
Policies related to the labor market such as labor laws, minimum wage, and unemployment support can have a considerable impact on employment rates. Supportive policies may help reduce unemployment and encourage more individuals to enter the workforce.The Impact of the Employment Rate on a Currency’s Value
The employment rate can have various effects on the value of a currency:1. Rising Employment Rate and Currency Appreciation
Strengthening Economic Growth:a high employment rate indicates economic prosperity and typically leads to increased demand for the currency.Expectations for Higher Interest Rates:With improving employment levels, the central bank may raise interest rates to support sustainable economic growth, thus making the currency more attractive in global markets.Boosting Investor Confidence:High employment signals economic stability, encouraging foreign investors to bring their capital into the country.2. Falling Employment Rate and Currency Depreciation
Slower Economic Growth:High unemployment often reflects underlying economic problems and can reduce demand for the currency.Easing Monetary Policies:a declining employment rate may prompt the central bank to lower interest rates in an effort to support the economy, which in turn diminishes the currency’s appeal.Increasing Market Uncertainty:High unemployment raises concerns among investors, potentially leading to capital outflows and weakening the currency’s value.3. Employment Reports and Currency Fluctuations
U.S. Non Farm Payroll (NFP) Report:This report is one of the most influential economic events impacting the forex market.Figures Above Forecast:Tend to strengthen the dollar.Figures Below Expectations:Usually lead to a weaker dollar.Supplementary Indicators:alongside the employment rate, indicators such as the labor force participation rate and average wages are also analyzed to gain a complete understanding of their impact on the currency.Conclusion
The employment rate indicator not only provides Forex traders with valuable insight into market direction but also assists policymakers in making more effective economic decisions. For a more comprehensive market analysis, it’s crucial to examine related reports such as NFP, labor force participation rate, and average wages alongside the employment rate. By leveraging these data points, traders and investors can make better-informed trading decisions and identify more profitable opportunities.

